Decentralized finance has transformed the financial landscape by offering individuals and institutions an alternative to centralized entities. Between 2008 and 2023, the DeFi space has amassed a whopping $50 billion. Nansen predicts the market will hit a gross revenue of $231 billion by 2030. However, like any financial market, DeFi presents significant risks such as regulation and security challenges. The way these challenges are managed today will determine the future of the crypto industry.
Why DeFi Security Deserves More Attention?
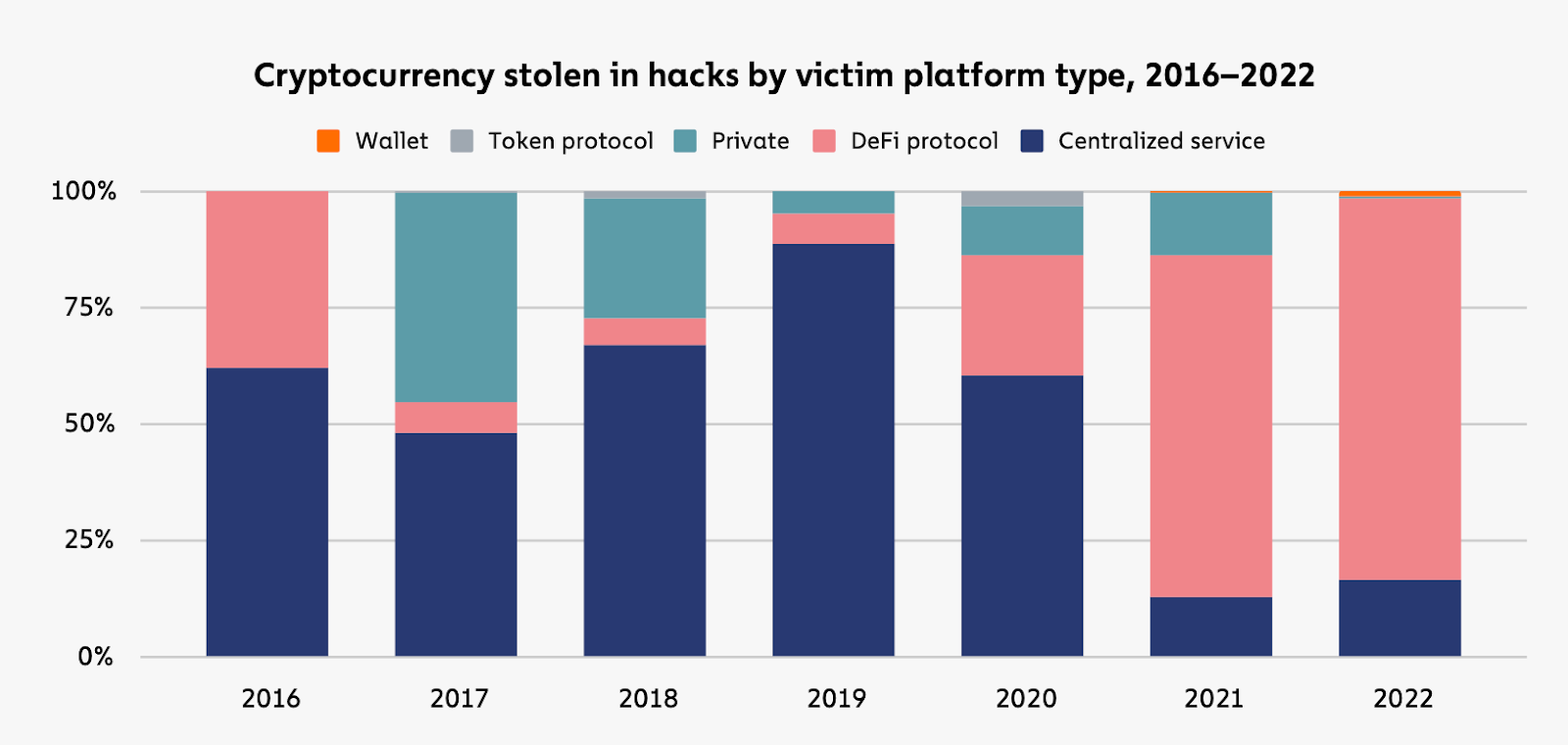
Increasing Value Hacked In DeFi
The increasing cash flow to DeFi has magnetized both good and bad actors. In a shocking 2016 DAO hack, the attacker stole over 3.6 million ether, currently around $60 million. The sums lost only got higher. In 2022, Binance Bridge was exploited for $570 million. The total amount hacked in DeFi has grown over the years, and the margin keeps increasing.
In 2022, a significant portion of cryptocurrency theft, amounting to $3.1 billion, was attributed to DeFi protocols, which accounted for 82.1% of the total stolen funds – yet another increase from the previous year’s 73.3%. Notably, 64% of the stolen funds were attributed to cross-chain bridge protocols.
? Follow @hackenclub on Twitter
Rapid Innovation
Compared to traditional finance, DeFi is still nascent. New protocols for infrastructure and user-centered solutions pop up every week. However, the race for rapid innovation can overshadow security concerns as founding teams strive to keep up with the fast-paced industry.
In DeFi, balancing the need for swift product development with comprehensive testing before deployment is crucial. But how can developers ensure both aspects are addressed effectively? The answer is community engagement, open-source libraries, and trusted security auditors.
The Complexity Of DeFi Applications
DeFi applications often require different tech stacks, money legos, and frameworks. Most applications depend on others for infrastructure.
Most DeFi apps use external libraries, i.e., dependencies. A single outdated or vulnerable dependency will expose all apps to the same security loophole.
A great example is the TimelockController.sol inside the OpenZeppelin Contracts library. The smart contract for a time-locked controller contained a critical vulnerability at some point, putting all dependent DeFi apps at risk.
Evaluating DeFi security goes beyond merely assessing the internal contracts. Auditing the underlying infrastructure and inherited components is essential to ensure a comprehensive analysis. Again, time-constrained founders don’t usually have time for that.
DeFi Security Risks
With millions of dollars at stake, a fast pace of innovation, and a decentralized, open-source architecture, DeFi protocols are an attractive target for hackers and scammers. People wanting to build a secure and sustainable DeFi ecosystem should pay attention to these risks:
Smart Contract Attacks
Smart contracts facilitate most of the transactions in crypto. Like other programs, smart contracts are only sometimes syntactically or logically perfect. Weaknesses in the codebase are natural.
Widespread vulnerabilities include flash loan attacks, oracle manipulation, and reentrancy. Even though smart contract developers do their best to write secure code, hackers still find their way in. For example, the most recent Deus DAO hack (May 5, 2023) was due to a vulnerability in a burn function.
The risks of exploits add uncertainty to mainstream adoption as users don’t want to put their money in Web3 apps that are hacked regularly.
Market Volatility And Manipulation
The crypto market is unstable. There’s no denying that. In the past two years, Bitcoin peaked at $60k, plummeted to $15k, and recovered to $30k in Q2 2023. Most other coins followed suit.
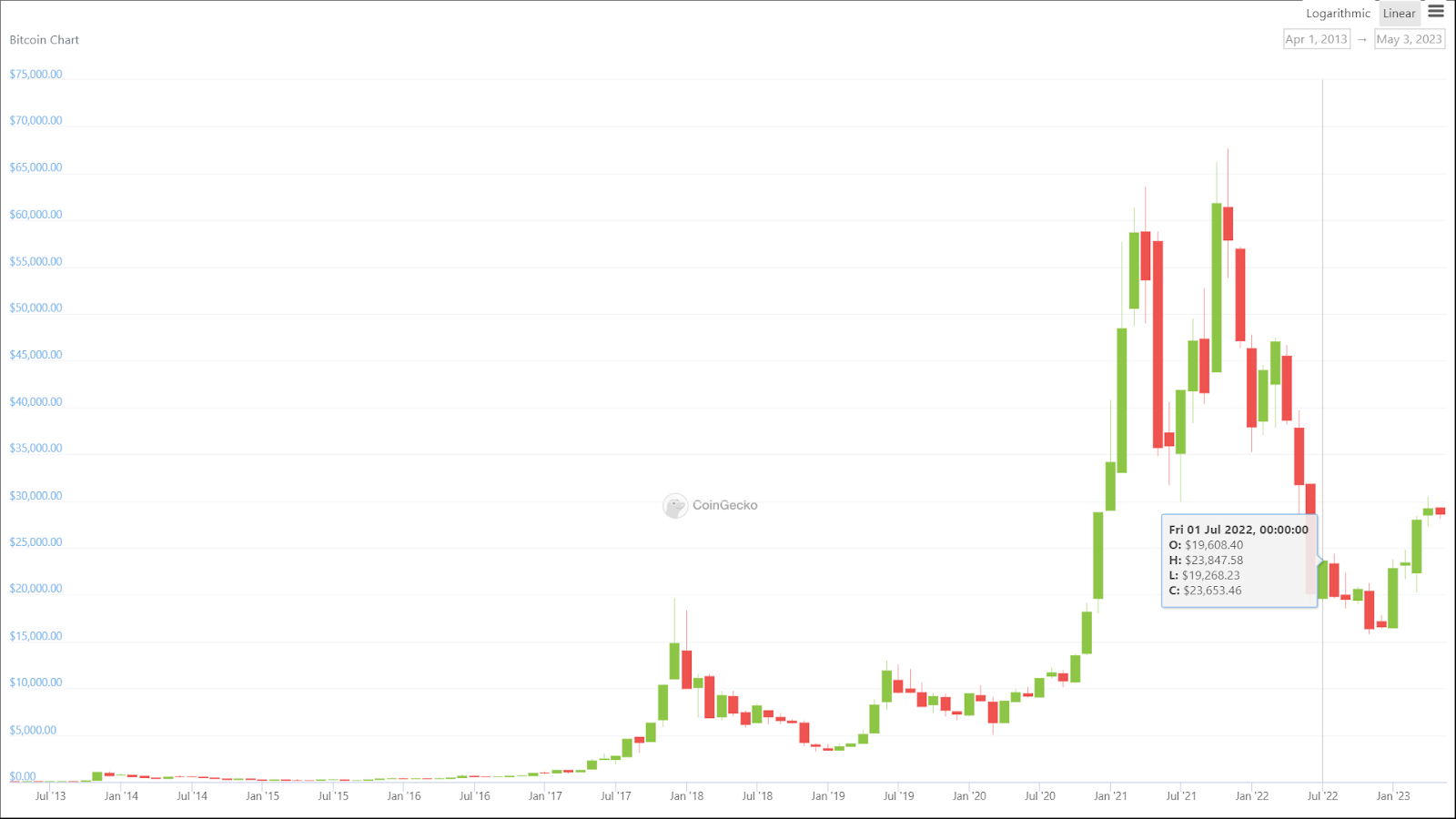
In addition to extreme volatility (all of us have come to accept), we have large crypto whales controlling the market. Also, there are scammers with their Ponzi schemes and outright insider traders.
On top of that, token issuers focus too much on distribution schedules, leaving little consideration for demand drivers. We’ve seen cases where poorly designed token economics created many problems, even fatal, to DeFi projects.
SafeMoon: Despite a seemingly reasonable burning mechanism to boost its price, demand for SafeMoon plummeted, leading to a 99.95% decrease in price, ultimately destroying the protocol's economy and community.
Axie Infinity: As a pioneer in play-to-earn gaming, Axie Infinity's excessive inflation resulted from inadequate sinks for its Smooth Love Potion, causing the token price to collapse by 99.95%.
Terra: Once a leading stablecoin, TerraUSD lost its peg due to a feedback loop that caused the price of LUNA, its native token, to drop significantly. This event led to a 100% decrease in value and insufficient liquidity to escape the collapsing market.
Regulatory Risks
The DeFi ecosystem operates in a regulatory gray area, which means that it is not clear how existing financial regulations apply to these protocols. This can create significant legal risks for entrepreneurs, investors, and users who may unknowingly violate laws or regulations.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been actively campaigning to regulate cryptocurrencies since 2017, arguing that it has the authority to oversee many digital coins and the platforms that trade them.
However, the SEC can only regulate digital coins that are classified as securities, a category that includes assets such as stocks and bonds. SEC Chair Gary Gensler has stated that most crypto tokens fall within that category, meaning many were distributed illegally because securities can only be sold to the public if they are registered with the SEC, and issuers provide financial and risk disclosures.
Working out the legal status of decentralized finance is in progress. For example, in 2020 the SEC filed a lawsuit against Ripple Labs, alleging that its XRP token was an unregistered security. This lawsuit has significant implications for the entire DeFi ecosystem since it could lead to more regulatory scrutiny and legal action against other tokens that may be deemed unregistered securities.
Moreover, lawmakers require crypto traders to have KYC policies to prevent the use of blockchain for money laundering and sanctions circumvention. DeFi projects should be aware of the legal environment in the countries of their residence to avoid any unnecessary troubles.
Governance Risks
Proper and absolute decentralization was one of the core promises of blockchain technology. The decentralization tenet must be entrenched first in its consensus mechanism — this goes on in the protocol layer of blockchains.
Most times, blockchains with Proof of Staked Authority or Proof of Authority consensus mechanisms tend to have relatively centralized outlooks. For instance, BNB Chain only has 50 validators, whereas Bitcoin has over 12,000 validators.
Recall that whatever the few validators decide will have a ripple effect on the DeFi protocols building on such chains.
In addition, malicious actors take over the blockchain to revert its stage. 51% attacks or Sybil attacks are rare but can still happen with new blockchains.
A protocol’s governance structure should also be designed to scale through the rainy days. For instance, the governance token of Maker DAO faced a palpable crisis during the rapid drop of ETH and the corresponding liquidation of the protocol’s governance tokens.
Trust And Reputation
Crypto is the land of rug pulls, and even the most credible players can flee with investors’ money. Recall SBF, who defrauded FTX users and laundered their funds. Also, the Africrypt exchange founders stole almost $4 billion in one of the most extraordinary rugs in crypto.
A tainted reputation is a recipe for disaster in DeFi, and the community is unlikely to give anyone a second chance. For example, no one really trusted Azuki founder Zagabond after he admitted the rug pull but promised to turn a new leaf.
Crypto traders and analysts can mitigate this risk through proper research and proving reserves and liabilities.
Best Practices For DeFi Security
Discarding DeFi because of its inherent risks is like unplugging the server to stop a single process. It’s better to come up with practical solutions based on the following best practices:
Conduct Regular Smart Contract Security Audits
Smart contract-related risks are one of the most dangerous weaknesses of DeFi. The leading solution to it is for protocols to get audited. Internal review or automated tools cannot fully substitute an independent external verification by a trusted third party.
The industry has matured beyond the point where Web3 projects underwent audits primarily for marketing purposes. Treating audits as a marketing ploy has proved insufficient for security. DeFi protocol hacks have occurred due to superficial audits prioritizing certification over a thorough security analysis. To that end, it is necessary to undergo relevant audits that cover as much scope as possible.
The ecosystem needs more high-quality and thorough audits to discover all levels of vulnerabilities and recommend hotfixes. We must also emphasize that auditing is not a one-time activity. The best practice is to conduct it regularly, especially after updating or adding new contracts.
Implement Multi-Signature Controls
Multi-signature is a wallet that requires several private keys to authorize transactions. The main reason behind multi-party access is to separate security and responsibility. For example, a multisig wallet may require at least 2 of 3 keys to transact. Most DeFi projects and protocols use multisig wallets as a treasury, allowing them to handle large amounts of cryptocurrency among several actors.
But there has been a security concern about the security of multisig solutions. In 2017, hackers exploited the loopholes in the multisig wallets of Parity and stole over $30 million. A similar occurrence happened in 2022 when the multisig scheme of Harmony was hacked, and the protocol lost around $100 million.
Smart contracts power multi-sig wallets, so using wallets with secure contracts is essential. Some of the most popular solutions are Argent Vault and Gnosis Safe. Also, improving security for multisig solutions is possible by incorporating quality control systems.
Use Secure Custody Solutions
A bulkier part of crypto is about the custody of assets. If the custody solution is insecure, the assets would be vulnerable to attacks.
Custody solutions can be cold storage, hot storage, third-party storage, or even institutional storage. Whatever the case, the best practice is that the custody solutions must be adequately tested and audited.
Methods of battle-testing the security can include the incorporation of 2FA, private keys, biometrics, and lots more.
Provide User Education
User education is crucial in the rapidly evolving crypto industry. Firstly, it enables users to understand the ecosystem better, allowing them to evaluate projects and invest in reliable ones while avoiding potential scams. Secondly, education empowers investors and traders to safeguard their assets, which is particularly important in DeFi, where users manage their investments.
DeFi protocols are encouraged to engage in educational campaigns, AMA sessions, workshops, etc., to raise awareness. All Hacken Partners get an additional platform to boost educational efforts. Greater understanding will help prevent users from falling victim to social engineering schemes and ultimately enhance the overall security of the ecosystem.
Use Insurance And Risk Management Solutions
Insurance is a sign of maturity. It is a cornerstone in the world of traditional finance because it puts risks further under control. Considering how unpredictable the crypto market is, it makes sense to be insured.
Insurance terms vary greatly, but the general idea is to compensate the damages when something goes wrong. It gives confidence and helps DeFi protocols recover in a cyber attack, depeg, or other covered cases. On top of that, having a treasury for emergencies – the so-called rainy day fund – can prove valuable too.
Foster Collaboration And Information Sharing
DeFi will not win if projects and protocols are playing a one-person show. There is a need for good collaboration and information sharing.
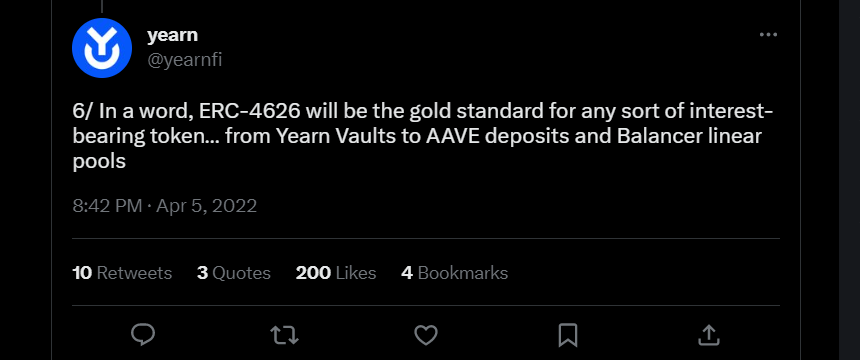
A good example is how Yearn Finance came up with the idea of ERC-4626 and shared it with the whole DeFi community. ERC-4626 introduces a long-awaited standardization and tighter security of vault systems and yield-bearing tokens.
Furthermore, DeFi protocols should foster transparency of their assets and liabilities to give users a sense of solvency. Indeed, being open about the valid rate of collateralization is the only way to gain community trust and operate successfully.
Crowdsourced Protection
As thorough as auditors should be, they can sometimes miss vulnerabilities. Getting another layer of protection in the form of bug bounty and other crowdsourced defense solutions makes sense because these security controls are cost-effective and are not bound in time.
There are a lot of whitehats who bug hunt various protocols. They discover and alert the team of any critical vulnerabilities. All big names, including Uniswap, Filecoin, and OpenSea, have bounty programs. A white hat hacker found a critical vulnerability in Arbitrum cross-chain functionality that could have cost millions for its users.
Bug bounty programs have gradually become best practices in the crypto sphere. You can easily set up your bug bounty program with Hacken Proof for free.
Having Legal Teams To Liaise With Regulators
While regulations are more pressing for CeFi, DeFi businesses should at least be aware of the general legal trends and comply with the relevant AML laws and other requirements, such as sanctions circumvention.
The top 3 crypto exchanges in trading volume—Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken—have solid legal teams. For DeFi, having a legal team makes sense as a precautionary measure.
Final Thoughts
DeFi offers tremendous potential for innovation and growth in the world of finance. However, this potential comes with significant risks and challenges that must be addressed to ensure the ecosystem's long-term success.
By understanding and addressing the risks outlined in this article and adopting best practices for DeFi security, entrepreneurs, investors, and Web3 business professionals can build a more secure, trustworthy, and inclusive financial system for the future.
? Follow @hackenclub on Twitter



