Liquidity pools are the backbone of decentralized finance (DeFi), powering everything from token swaps to lending protocols. It’s the technology behind billions of dollars traded on blockchains. Understanding the fundamentals behind liquidity pools and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) is crucial for anyone in the space to understand the essence of DeFi.
This article delves into the mechanics of liquidity pools, explores their benefits and risks, and provides essential security tips for participants.
What Is a Liquidity Pool?
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptocurrency tokens or assets locked in a smart contract. These pools are the foundation for decentralized trading, lending, and other financial services, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries. In DeFi, liquidity pools enable 24/7 trading, automated price discovery, and opportunities for passive income through liquidity provision.
How Do Liquidity Pools Work?
Liquidity pools operate on a relatively simple principle but power complex financial interactions. They are not limited to DEXs only and serve as a foundational backbone for various DeFi use cases.
- Liquidity Providers (LPs) are users who deposit pairs of tokens into the poo. Typically, that’s equal value, but it can also have different values depending on the model underlying the smart contracts. For example, an ETH/USDC pool would require depositing equal values of USD of both Ethereum and USDC.
- Automated Market Makers (AMMs) are the underlying smart contracts that use mathematical formulas to determine asset prices and facilitate trades. The most famous one is Uniswap’s constant product formula (x * y = k), which maintains balance in the pool. With new models, those formulas have been upgraded to serve other functions.
- Other types of Liqudity Pools do exist in DeFi, serving, for example, lending protocols and NFT projects. While not necessarily using the AMM model, these protocols are still considered liquidity pools where users earn rewards for depositing tokens.
- Fees and Rewards: LPs earn a portion of the trading fees generated by the pool. Some protocols also distribute governance tokens or offer yield farming opportunities as additional incentives.
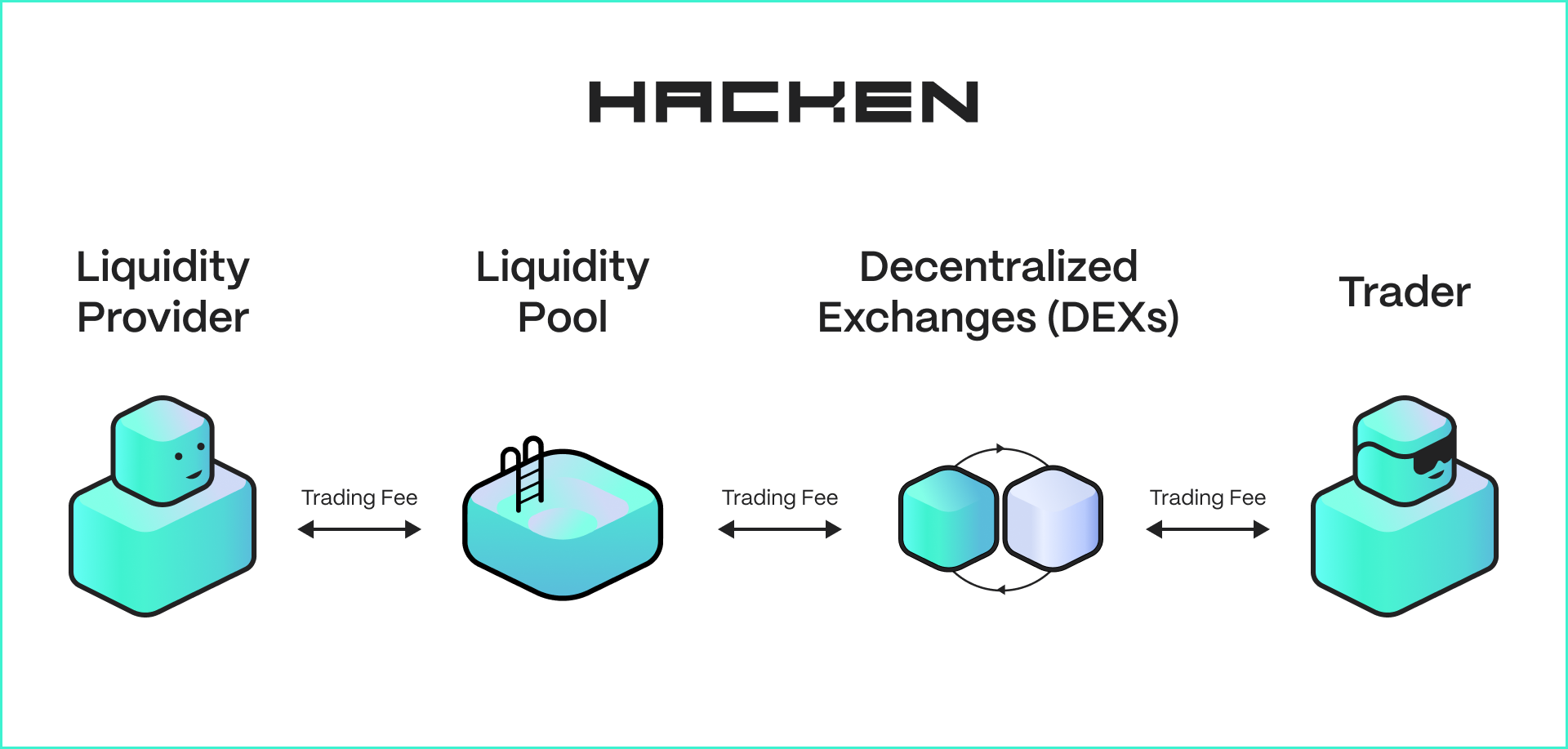
When users want to trade, they interact with the liquidity pool rather than a traditional order book. The AMM calculates the exchange rate based on the current ratio of assets in the pool, ensuring there's always liquidity available for trades.
Benefits of Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools offer several advantages over traditional market-making systems:
- Decentralization: Anyone can become a liquidity provider, democratizing market-making.
- Continuous Liquidity: Pools enable 24/7 trading without the need for matching buyers and sellers.
- Efficient Price Discovery: AMMs automatically adjust prices based on supply and demand within the pool.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: New projects can easily create trading pairs and gain liquidity without relying on centralized exchanges.
Yield Farming & Liquidity Pools
Yield farming, also known as liquidity mining, is a strategy where users provide liquidity to pools in exchange for rewards. These rewards often come in the form of the platform's native token, creating a symbiotic relationship: users provide liquidity, and in return, they receive tokens that give them a stake in the platform's governance and future success.
Unlike AMM, where users earn from the fee taken on trades, yield farming offers extra rewards through token inflation. Yield farming protocols often incorporate more complicated tokenomics in an attempt to attract yield.
Types of Liquidity Pools
Different DeFi platforms have innovated on the basic liquidity pool concept and today liquidity pools form various types for various purposes:
- Traditional Pools (e.g., Uniswap v2, SushiSwap): Two-token pools with a 50/50 value ratio.
- Stablecoin Pools (e.g., Curve Finance): Designed for low-slippage trades between assets of similar value.
- Multi-asset Pools (e.g., Balancer): Allow for pools with more than two assets and custom ratios.
- Single-sided Liquidity (e.g., Bancor): Users can provide liquidity with just one token, reducing impermanent loss risk.
- Concentrated Liquidity (e.g., Uniswap v3): LPs can focus their capital within specific price ranges for higher efficiency.
Most Popular Liquidity Pool (DEX) Platforms
While the DEX landscape is evolving, many foundational exchanges are still popular today.
It is important to know that each blockchain needs its DEX because liquidity will be isolated on that specific blockchain. The lack of interoperability protocols is partly the reason. Today, however, the EVM world is often converging away from fragmentation, and one example of this is cross-chain swaps facilitated by several of these exchanges below.
- Uniswap: The pioneer of AMM-based DEXs, known for its simplicity and large liquidity.
- Curve Finance: Specialized in stablecoin swaps with low slippage.
- Balancer: Offers customizable multi-asset pools.
- SushiSwap: A fork of Uniswap that introduced additional yield farming incentives.
- PancakeSwap: The largest DEX on the Binance Smart Chain.
DEX aggregators also exist, which are interfaces that connect liquidity pools together and create a unified trading interface.
Liquidity Pool Risks
While liquidity pools offer numerous benefits, they also come with considerable risks:
- Impermanent Loss: The primary risk for LPs, occurring when the price ratio of pooled assets changes.
For example, if one token in a pair significantly outperforms the other, LPs may have been better off simply holding the tokens. This means that when providing liquidity using two assets and the price of one asset rises, the amount of tokens in the pool is rebalanced from each other so that both asset pools are equal to the same value in the initial stage.
As the price moves, there is more of the less valuable asset in the pool because people are essentially selling it to you. This means that if you withdraw your assets at that time, you will receive less of the valuable token than you initially committed, potentially resulting in a loss compared to simply holding the assets in your wallet. - Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs or exploits in the underlying smart contracts can lead to fund loss. The 2020 Harvest Finance hack resulted in a $33.8 million loss due to a flash loan exploit.
- Rug Pulls: Malicious actors can create pools with fraudulent tokens, drain liquidity, and disappear. The AnubisDAO incident in 2021 saw investors lose $60 million in such a scheme.
Security Measures for DEXs and Liquidity Pools
When you want to trade on a DEX through liquidity pools, several security best practices must be followed to ensure the safety of your assets.
To mitigate risks, you can:
- Use Audited Platforms: Stick to well-established protocols that have undergone multiple security audits. Platforms like Uniswap and Curve have proven track records (however, they are NOT hack-proof).
- Implement Multi-signature Wallets: For projects managing large liquidity pools, using multi-sig wallets adds an extra layer of security against unauthorized withdrawals.
- Consider Insurance: Protocols like Nexus Mutual offer coverage against smart contract failures.
- Diversify: Don't put all your assets into a single pool or platform.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest DeFi news and be aware of potential vulnerabilities or exploits.
- Use Security Tools: Implement tools like Tenderly or Defender for real-time monitoring of smart contract interactions.
- Thorough Due Diligence: Before providing liquidity, research the project thoroughly. Check the team's background, the token's tokenomics, and the protocol's security measures.
Check out this article: DeFi Security: Understanding And Addressing Risks In The Future Of Finance
Conclusion
Liquidity pools are a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem, enabling decentralized trading and yield generation. While they offer exciting opportunities, users must approach them with caution and a solid understanding of the underlying mechanics and risks. Prioritizing security is crucial for anyone looking to participate in this innovative financial landscape.



