- ERC-4337 revolutionizes account management by introducing smart accounts, transforming them into "smart wallets". This enhances functionality, security, and user experience.
- ERC-4337 enhances security by allowing multiple signature requirements and simplifying the recovery process, ensuring self-sovereignty and mitigating the risk of account loss.
- ERC-4337 enhances intelligent fee management which allows sponsored transactions and transaction fees to be paid in ERC-20.
- ERC-4337 provides account abstraction without any consensus layer changes by using an alternative mempool.
Account Abstraction: Smart Account vs EOA Account
Account abstraction is revolutionizing account management in the blockchain ecosystem by introducing the concept of smart accounts. Unlike traditional Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs), smart accounts enable users to utilize smart contracts as their primary accounts, transforming them into "smart wallets". Moreover, the adoption of account abstraction through initiatives like ERC-4337 in the Ethereum ecosystem represents a transformative shift, providing enhanced security features, new functionalities, and an improved user experience.
Smart accounts, enabled by account abstraction, are a significant leap forward in blockchain account management. Account abstraction aims to enhance functionality and security by enabling the direct execution of functions from wallets, thereby eliminating the need for external interactions. This streamlined user experience seamlessly integrates smart contract capabilities into everyday transactions.
Intelligent fee management is a notable feature introduced by account abstraction. Wallets equipped with this capability can determine optimal transaction fees and assign fee payment responsibility. This empowers users with increased flexibility and efficiency in managing transaction costs.
Security is greatly strengthened through account abstraction. It enables multiple signature requirements for transactions, providing an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access and potential attacks. Moreover, the recovery process is simplified, reducing reliance on centralized assistance. Users can regain control over their accounts independently, ensuring self-sovereignty and mitigating the risk of account loss.
Difference Between Account Abstraction And ERC-4337
While ERC-4337 brings significant advancements to account functionality and transaction fee management, it does not achieve complete account abstraction. Unlike true account abstraction, ERC-4337 functions more as a transaction relayer, offering an off-chain order book for organizing transactions before relaying them to the blockchain.
However, true account abstraction envisions a more comprehensive transformation in the way Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) interact with the Ethereum blockchain itself. Achieving this level of abstraction requires a substantial upgrade to Ethereum's entire consensus mechanism, a complex undertaking that goes beyond the scope of ERC-4337.
While other EIPs were already published to reach account abstraction, they required some protocol changes in the consensus layer. ERC-4337 aims to provide account abstraction without any consensus layer changes.
An account abstraction proposal which completely avoids consensus-layer protocol changes, instead relying on higher-layer infrastructure.
How It Works (Technical Explanations)
The ERC-4337 standard introduces a new object called "UserOperation" to the Ethereum network, enabling the functionality of smart wallets. When a user initiates a UserOperation, the “higher-layer pseudo-transaction object” is sent to a separate mempool specifically designated for processing ERC-4337 transactions, distinct from the main Ethereum network's mempool.
One of the key advantages of ERC-4337 is the increased flexibility it offers compared to the mainnet. Users can perform multiple transactions at once, bundling them together within a UserOperation. Additionally, users can delegate the payment of transaction fees to an Externally Owned Account (EOA), such as a wallet provider, streamlining the process and reducing user fees.
The process of utilizing ERC-4337 involves four stages:
- The user expresses their intent by creating a UserOperation, representing their desired transaction. These UserOperations are akin to unconfirmed transactions.
- Bundling these UserOperations into the separate mempool designed for ERC-4337 transactions, where Bundlers (validators) handle them.
- The bundled transactions are sent to the EntryPoint contract, a standardized piece of code that acts as a reference point on the blockchain.
- The EntryPoint calls the validateUserOp function to identify the UserOperation associated with the contract wallet. The smart contract wallet should implement the ExecuteUserOp function to ensure the completion of the transaction.
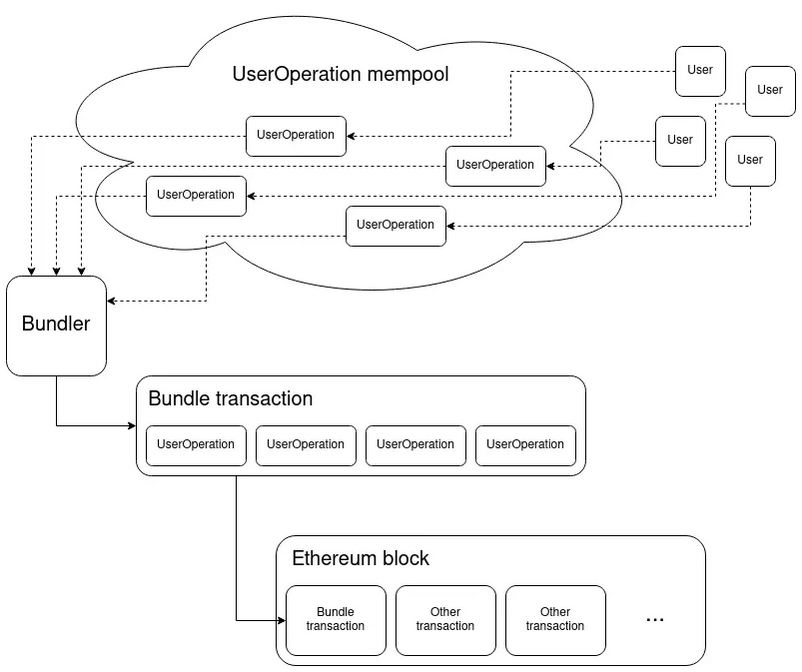
Diagram from Vitalik Buterin
It's important to note that the ExecuteUserOp fees can be paid using the "ETH Balance" element associated with the smart contract wallet or any other ERC-20 token. In the case of sponsored transactions, a PayMaster with ETH Balance can validate and pay the gas fees. Additionally, if the transaction involves multiple signatures, Signature Aggregators can come into play to facilitate the execution.
For detailed technical information, see https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-4337
Features
The ERC-4337 will bring the possibility to add new features that will have a major impact on User Experience and mass adoption.
1. Performing multiple actions in one transaction: The ERC-4337 standard allows bundling multiple transactions into a single transaction, streamlining the process and reducing the need for multiple sign-offs. This feature is particularly beneficial for traders and gamers who frequently perform multiple actions within a single interaction.
2. Performing one transaction with multiple people (multisigs and social recovery): ERC-4337 enables the execution of transactions that require multiple signatures, allowing for collaborative decision-making and increased security. Additionally, it introduces the concept of social recovery, where designated guardians or accounts can assist in account recovery if the user loses their seed phrase or encounters access issues.
3. Paymaster (sponsored transactions and erc20 paid transactions): With ERC-4337, users can benefit from sponsored transactions, where a third-party entity such as a dApp or wallet provider covers the transaction fees on behalf of the user. Furthermore, the standard allows payment of gas fees using ERC-20 tokens, providing more flexibility and reducing dependency on a specific token for transactions.
4. Subscription, limits, and automated payments: The ERC-4337 standard supports automated and recurring payments, enabling subscription-based models and facilitating seamless transactions for services like online subscriptions or recurring payments. Users can define custom spending limits and usage instructions, setting alerts and notifications for specific thresholds or criteria.
5. A more seamless user experience: By incorporating features such as pre-approval and auto-approve transactions, ERC-4337 enhances the user experience, reducing friction and making interactions with smart wallets and blockchain applications more intuitive and efficient. This is particularly advantageous for blockchain gaming and other user-centric applications.
6. More efficient and simpler signature algorithms: The ERC-4337 standard promotes the adoption of more efficient and simpler signature algorithms like Schnorr and BLS, which offer improved performance and reduced complexity compared to traditional signature schemes. These algorithms enhance the speed and efficiency of transaction processing on the blockchain.
7. Post-quantum safe signature algorithms: To address future cryptographic threats, ERC-4337 explores the integration of post-quantum safe signature algorithms like Lamport and Winternitz. By incorporating these algorithms, smart wallets become more resilient to potential attacks from quantum computers, ensuring the long-term security of user assets.
8. Upgradeability: ERC-4337 supports the concept of upgradeability, allowing for the introduction of new features, improvements, and bug fixes without disrupting the existing ecosystem. This feature enables the blockchain network and smart wallets to evolve over time, adapting to emerging technologies and user needs while maintaining compatibility with previously deployed contracts and wallets.
Benefits vs Risks
Benefits of ERC-4337
1. Verification logic flexibility: The ERC-4337 standard provides flexibility in the validation logic by allowing the addition of arbitrary signature and nonce verification mechanisms. This enables the integration of new signature schemes, multisig functionalities, and other custom verification processes, enhancing the security and versatility of smart wallets and transactions.
2. Sufficient to make the execution layer quantum-safe: Universal adoption of ERC-4337 eliminates the need for further modifications in the execution layer to achieve quantum-safe security. Users can individually upgrade their wallets to quantum-safe versions, ensuring the safety of their transactions. Additionally, the use of hash-protected externally owned accounts (EOAs) for each bundled transaction adds an extra layer of protection against quantum attacks.
3. Wallet upgradeability: ERC-4337 allows wallet verification logic to be stateful, enabling wallets to change their public keys or upgrade their entire code through the use of DELEGATECALL. This upgradeability feature enhances the flexibility and adaptability of smart wallets, facilitating the integration of new functionalities and improvements without disrupting the existing infrastructure.
4. Execution logic flexibility: With ERC-4337, smart wallets gain the ability to incorporate custom execution logic, enabling atomic multi-operations and enhancing the execution step's flexibility. This supports complex transaction sequences and facilitates the achievement of atomicity, where multiple operations are executed as a single indivisible unit, providing more sophisticated transaction capabilities.
Risks of ERC-4337
1. Slightly increased DoS vulnerability: The introduction of more complex verification logic in ERC-4337 brings a slightly higher risk of potential denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. The increased complexity may provide additional attack vectors, requiring careful consideration and thorough testing to mitigate any potential vulnerabilities and ensure the overall security of the system.
2. Gas overhead: Compared to regular transactions, ERC-4337 transactions may involve slightly more gas overhead due to the added functionality and flexibility provided by the standard. However, this additional gas cost is often offset by the benefits gained, such as support for multi-operations or the ability to upgrade wallets, making it a trade-off between functionality and gas efficiency.
3. One transaction at a time: ERC-4337 limits the ability of accounts to queue and send multiple transactions into the mempool simultaneously. While the standard supports atomic multi-operations within a single transaction, the restriction on queuing multiple transactions may pose a limitation in certain use cases where simultaneous or batched transactions are required. However, the atomic multi-operation feature mitigates the need for simultaneous transactions in many scenarios, reducing the impact of this limitation.
Conclusion
The advent of account abstraction and the implementation of ERC-4337 in the Ethereum ecosystem mark significant milestones in the evolution of blockchain technology.
Smart accounts, empowered by account abstraction, offer improved functionality, streamlined user experience, enhanced security, and quantum-resistant cryptography. Although ERC-4337 does not achieve complete account abstraction, it introduces many features that could drastically improve user experience and pave the way to mass adoption.
It is worth noting that Visa is actively experimenting with account abstraction through ERC-4337, incorporating paymaster functionality in the testnet while Pimlico has recently launched its own implementation on mainnets. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the ERC-4337 standard holds immense potential for transforming how users interact with the blockchain and bringing mass adoption.



